
Have you ever saved a document online or used an app without installing it? If so, you’ve already experienced cloud computing without even realising it. As technology evolves, the way we store, access, and process data is changing and cloud computing is at the heart of this transformation.
In simple words, cloud computing is the practice of using the internet to access computing services such as storage, servers, databases, software, and more, without needing to own or maintain physical infrastructure.
Instead of keeping everything on your computer or local server, cloud computing allows you to work from virtually anywhere, using services hosted in secure data centres around the world.
This blog aims to explain what cloud computing is, how it works, the types available, and why it’s becoming an essential tool for businesses and individuals alike.
What Does Cloud Computing Really Mean?
At its core, cloud computing is a method of accessing technology resources via the internet. These resources include physical infrastructure such as servers and storage as well as virtual IT services like software applications and processing power.
The “cloud” is simply a metaphor for the internet. In traditional computing, users install software and save files locally on their devices.
In contrast, cloud computing stores data on remote servers managed by a third party, allowing users to access their information from any device with internet connectivity.
This approach supports a more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way of operating, particularly for businesses looking to adapt quickly to changes in demand and technology.
How Did Cloud Computing Begin?

The concept of centralised computing has existed since the 1960s when large mainframe computers were shared by multiple users.
However, the modern era of cloud computing began in the early 2000s when technology companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google launched commercial cloud platforms.
These developments laid the foundation for a market that now powers everything from streaming services and e-commerce websites to global supply chains and government databases.
| Year | Milestone |
| 2002 | Amazon launches AWS (Amazon Web Services) |
| 2006 | Google introduces Google Docs |
| 2010s | Cloud adoption accelerates across sectors |
| 2020+ | COVID-19 drives mass migration to the cloud |
How Does Cloud Computing Actually Work?
Cloud computing relies on a layered architecture that separates user-facing components from backend operations. This architecture includes:
- Front-End Interface: The software or application a user interacts with, such as a web browser or mobile app.
- Back-End Infrastructure: Servers, storage systems, databases, and software that perform the heavy lifting of data processing and management.
- Middleware: Software that facilitates communication between the front-end and back-end layers, ensuring smooth data transfer and system integration.
When a user accesses a cloud service—whether uploading a document to Google Drive or streaming a video on Netflix—their device sends a request to a cloud server. That server processes the request, retrieves or manipulates data, and sends the result back to the user, often in milliseconds.
What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing Models?
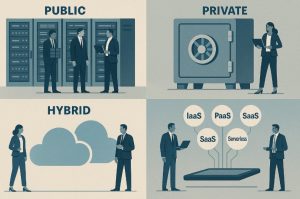
Cloud computing models are broadly divided into two categories: deployment models and service models. These models define how the cloud is accessed and what level of control the user has over the infrastructure.
What Are the Different Cloud Deployment Models?
| Model | Description | Suitable For |
| Public Cloud | Operated by third-party providers. Resources are shared among many clients. | Start-ups, SMEs, and freelancers |
| Private Cloud | Dedicated to one organisation, offering more control and security. | Large enterprises, government bodies |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines public and private clouds for flexibility. | Businesses with mixed IT needs |
What Are the Main Cloud Service Models?
| Model | Full Form | Function |
| IaaS | Infrastructure as a Service | Offers virtual servers, storage, and networking on-demand |
| PaaS | Platform as a Service | Provides a development platform for building and deploying applications |
| SaaS | Software as a Service | Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis |
| Serverless | Serverless Computing | Executes backend functions without managing server infrastructure |
Where Do We Use Cloud Computing in Everyday Life?
Cloud computing has become so integrated into daily life that many users may not even realise they are relying on it. Services such as email, online storage, media streaming, and collaborative tools all operate on cloud platforms.
For example, when using Gmail, your emails are stored on Google’s servers rather than your personal device. Similarly, tools like Google Docs, Microsoft OneDrive, and Zoom use cloud infrastructure to store data, manage user access, and deliver content in real-time.
In a business context, cloud platforms allow employees across various locations to collaborate on documents, manage workflows, and communicate efficiently, improving both productivity and operational agility.
What Are the Key Benefits of Cloud Computing?
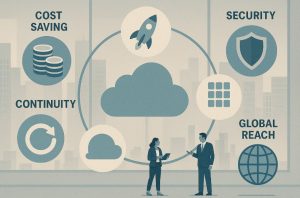
The rapid adoption of cloud computing can be attributed to the multitude of advantages it offers over traditional IT infrastructure. Some of the most compelling benefits include:
How Does Cloud Computing Improve Cost Efficiency?
Cloud computing significantly reduces capital expenditures by eliminating the need to purchase servers, software, and data centres. Instead, businesses pay only for the resources they use, typically on a subscription or usage basis.
How Does Cloud Computing Enhance Speed and Agility?
Resources can be deployed in minutes, allowing businesses to respond quickly to market demands. Cloud environments support continuous integration and deployment, helping companies release new features faster.
How Does Cloud Computing Support Scalability?
Organisations can scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand without the need for physical upgrades. This is particularly beneficial during peak periods or business expansion.
What Security Measures Are Provided by Cloud Providers?
Top-tier cloud providers implement stringent security measures, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with regulatory standards. Security protocols are often more advanced than what small to mid-sized businesses could implement on their own.
How Does Cloud Computing Ensure Business Continuity?
Cloud-based backups and disaster recovery solutions ensure that data is protected and recoverable even in the event of hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
How Does Cloud Computing Enable Global Reach?
Cloud services can be delivered from multiple data centres around the world, reducing latency and improving performance for users in different geographic regions.
How Is Cloud Storage Different from Cloud Computing?
While both cloud storage and cloud computing operate on similar principles, they serve distinct purposes.
| Feature | Cloud Storage | Cloud Computing |
| Primary Use | Storing and retrieving files | Running applications and processing data |
| User Interaction | File uploads, downloads, backups | Development, deployment, analytics |
| Examples | Google Drive, Dropbox, iCloud | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform |
| Resource Management | Minimal (user uploads and accesses files) | Extensive (user can configure environments) |
Cloud storage is a subset of cloud computing, focused specifically on data retention and access.
What Is the Future of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing continues to evolve with new trends shaping its trajectory. In India and globally, businesses are increasingly embracing advanced technologies powered by the cloud.
Key developments include:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud platforms offer scalable environments to develop and deploy intelligent solutions.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency and bandwidth use.
- Serverless Architecture: This allows developers to focus solely on code, improving efficiency and reducing operational overhead.
- Virtual Desktops: With remote work becoming standard, cloud-hosted desktops offer secure, flexible work environments.
- Multi-Cloud Strategies: Businesses are adopting a mix of providers to reduce risk and avoid vendor lock-in.
These trends indicate that the future of cloud computing lies in increased automation, decentralisation, and specialisation, providing more tailored solutions across industries.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing?

While the cloud offers numerous advantages, it is not without challenges. Understanding both is essential for making informed decisions.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go model reduces capital expenses | Subscription costs may add up over time |
| Flexibility | Access services from anywhere via the internet | Requires a reliable internet connection |
| Performance | Utilises powerful, scalable infrastructure | Service outages may affect availability |
| Security | Robust measures by providers | Still dependent on provider’s compliance and protocols |
| Control | Users manage apps and services easily | Limited control over the infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Automatic updates and patches | Dependency on third-party vendors for updates |
How Can Cloud Computing Be Explained in a Nutshell?
Cloud computing can be described as a model that enables users to access and utilise computing services such as storage, processing, and applications via the internet. It removes the need for physical infrastructure, making operations more agile, scalable, and cost-effective.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur running an online store, a student backing up assignments, or a software developer deploying code, cloud computing is quietly powering your digital experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes cloud computing different from traditional IT systems?
Unlike traditional IT systems that require physical infrastructure, cloud computing offers services over the internet, reducing costs and setup time.
How do businesses in India benefit from cloud adoption?
Cloud computing allows Indian businesses to scale quickly, reduce costs, and access advanced technologies without significant upfront investments.
Is cloud computing safe for storing sensitive data?
Yes, when managed correctly. Leading providers offer encryption, authentication, and monitoring to protect sensitive information.
What is the role of cloud computing in remote work?
Cloud platforms support collaboration tools, virtual desktops, and shared storage, making them ideal for remote work scenarios.
Can a business use both public and private clouds?
Yes. A hybrid model allows businesses to balance security and cost-efficiency by using both public and private clouds.
How does serverless computing help developers?
It abstracts infrastructure management, letting developers focus purely on writing and deploying code.
Are there any hidden costs in cloud computing?
Some providers charge extra for data egress, advanced features, or exceeding usage limits. It’s important to read the pricing details carefully.